The heart: Its structure and functioning
The normal heart is a strong muscular pump, a little bit larger than a fist. It continuously pumps blood throughout the circulatory system. Each day a heart beats (it expands and contracts) 100,000 times and it pumps 2,000 gallons of blood. In a 70-year lifetime, it beats more than 2,500 million times.
The circulatory system is the net of elastic tubes that transport blood to the entire body. It includes the heart, lungs, arteries, arterioles (smaller arteries) and capillaries (very small blood vessels). These blood vessels transfer blood rich in oxygen and nutrients to the whole body. The circulatory system also includes venules (small veins) and veins. These are the blood vessels that transport blood without oxygen back to the heart and lungs.If all these blood vessels were to be lined-up linear from end to end, they would extend 60,000 miles. This is enough to circle the earth more than twice.
The circulating blood transports oxygen and nutrients to all the organs and tissues of our organism, including the heart. Blood also collects waste products from our body’s cells. These waste products are disposed of through the filtering processes of the kidneys, liver and lungs.
Anatomy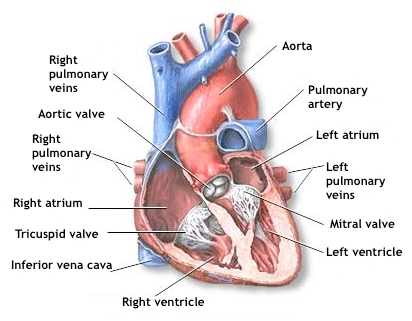
The heart has four chambers through which it pumps blood. The two upper ones are the left and right auricles. The two lower ones ar the left and right ventricles. Four valves open and close to let blood flow only in one directions when the heart beats:
- The tricuspid valve sits between the right auricle and the right ventricle.
- The pulmonary valve sits between the right ventricle and the right pulmonary artery.
- The mitral valve sits between de left auricle and the left ventricle.
- The aortic valve sits between the left ventricle and the aorta artery.
Each valve has a set of flaps (also called leaflets). The mitral valve has two leaflets. The others have three. Under normal conditions, the valves let blood flow only in one direction. Blood flow occurs only when there is a difference in pressure that makes them open.
How does it pump blood?
The four heart chambers must beat in an organized manner. This is controlled by electrical impulses. A heart chamber contracts when an electrical impulse travels through it. The signal starts ate the sinoatrial nodule, also called sinus nodule, which consists of a small bunch of highly specialized cells in the right auricle. A discharge from this natural pacemaker makes the heart beat. This pacemaker generates electrical impulses at a predetermined frequency. However, emotional reactions and hormonal factors may affect the frequency of discharge allowing the heartbeat frequency to respond at different demands.

